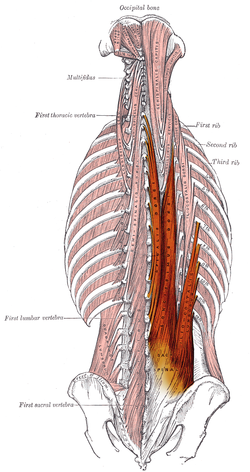
胸腰肌筋膜是人體後側一片極為重要的結構
在漫長的演進過程中, 胸腰肌筋膜協助了直立姿勢以及傳遞核心到上下肢的力量
在我們行走的動作中扮演了不可或缺的重要角色
Thoracolumbar fascia (TLF) is a crucial structure at the back of our trunk
With the human evolving,
TLF helps us keeping the upright and transmitting force from core to extremities.
It plays an important role in our daily life especially walking.
 |
| Neumann, page 362 |
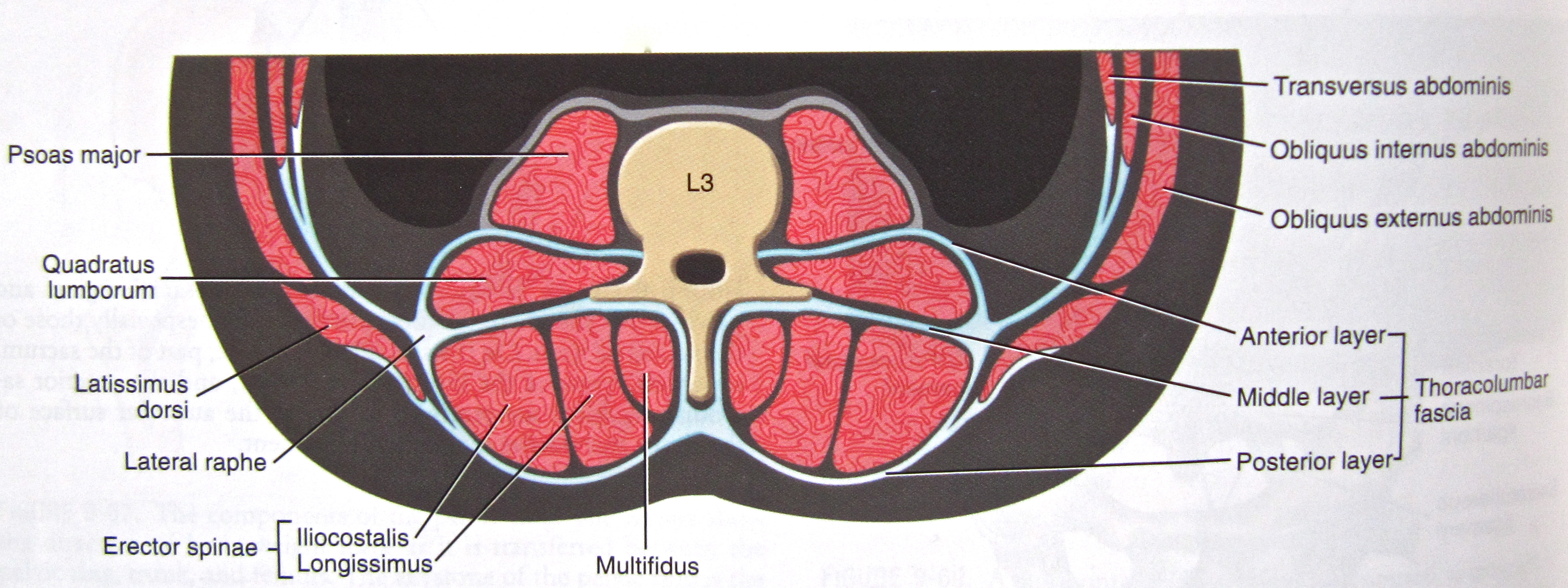
在近代的多數研究中
將胸腰肌筋膜分為三個部分: 腹層, 中層, 以及背層
多數時候我們看到的菱形狀筋膜只代表了後層的筋膜
實際上整個胸腰肌筋膜在不同層有著不同方向的走向, 是一個多面向的支撐結構
請記得筋膜組織本身相較於韌帶肌腱是一個較不規律的結構
但長期的姿勢與習慣可以造成漸進性的方向變化
In most research, TLF is described as a three-layer system: anterior, middle, and posterior.
The diamond-shape we are used to seeing is just showing the posterior layer of TLF.
In fact, the TLFhas many different directions within different layers.
It's a multiple-supporting structure.
Remember the fascia is a less regular structure compare to the ligament or tendon.
The long-term posture and habit can cause the gradual change on it.
下面使用的伸展方式主要以背層為主, 從兩個面向切入:
1. 中央神經系統CNS:
利用魯菲尼受器(Ruffini receptor)傳遞訊息到中央神經系統, 藉此改變筋膜與周遭組織張力
2. 自主神經系統ANS:
利用呼吸以及間質受器(Interstitial receptor)傳遞訊息給自主神經系統
調控筋膜內的血管壓力與平滑肌組織
The following stretches mainly focus on the posterior layer.
Two concepts will be integrated into stretching:
1. Central Nervous System, CNS:
Ruffini receptor will send a message to the CNS to regulate the tension of fascia and surrounded tissue.
2. Autonomous Nervous System, ANS
Breathing and interstitial receptor can affect ANS that regulates the vessel pressure and smooth muscle in the fascia.
 |
| Schleip R 2003: Fascial plasticity – a new neurobiological explanation. Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies |
綜合上述生理學看法, 靜態伸展絕對不是伸展筋膜的好方法
Base on those physiology concepts, the static stretch in not a good idea for fascia.
第一種伸展方式使用土耳其起立(Turkish get-up)的起始姿勢
The first stretch is the starting position of Turkish get-up
 |
| https://squatuniversity.com/tag/squat-university/ |
吐氣時收縮核心, 利用呼吸誘發ANS反映以及使用核心增加胸腰肌筋膜張力
手肘與腳底頂地, 利用臀大肌與闊背肌增加胸腰肌筋膜張力
然後吸氣產生360度的軀幹擴張並且放鬆,
可以在腰部使用一個伸展球或網球產生深層慢速的壓力去刺激肌間質受器
Breath out to facilitate core.
Using breathing to affect ANS and core to increase the tension of TLL.
Elbow and feet against the ground, increasing tension by activating Glu Max and Latissmus Dorsi.
Then breath in to create 360-degree expansion and relax.
You can further put a stretch ball or tennis ball to create a deep and slow pressure to stimulate interstitial receptor.
另一種伸展方式利用鳥狗式(Bird-dog)
需要比較好的核心與身體控制能力
The other stretch is more dynamic via the Bird-dog exercise
This one needs better core and body control ability.
 |
| https://howtoloseweight.com.pk/easy-exercises-lose-stubborn-back-fats/ |
在手肘碰觸膝蓋過程中, 同時加入吐氣與脊椎屈曲的動作
回復姿勢時吸氣同時加入臀肌與背肌的啟動來增加筋膜張力
While your elbow touch you knee, breath out and bend your spine to create more stretch.
Back to the posture above and engage Glu muscles and back muscles to load TLL.
當然放鬆筋膜的方式不是只有這兩種方式
但要特別注意肌肉與筋膜的伸展需要考量到不同受器的影響
如果你能合法的執行徒手技術, 在加壓的同時給予主動動作會有很好的效果
下次我會更深入的談談已知關於筋膜我們所了解的東西
想要更進階的了解筋膜的生理反應與解剖意義請關注這系列的文章
Of course there's more way to stretch your TLF.
Just need to know there're many receptor actions need to be considered in different soft tissues.
If you can perform manual technique legally, you can achieve an amazing result by pressure with active movement.
Next time I'll discuss deeper about what we know about TFL so far.
If you're interested in advanced physiology and anatomy of TFL,
I'd like to share it once I gather all the materials I need.
有沒有正確的執行以及適不適合這個人執行才是最大的關鍵
Every exercise or treatment has the same concept
"The keys are accuracy and adequacy "
本著作由I-Chen Liu, PT, MS製作,以創用CC 姓名標示-非商業性-相同方式分享 4.0 國際 授權條款釋出。